Acoustic vs Digital Accordions: Sound, Texture, and Innovation
The accordion's evolution balances traditional craftsmanship with modern technology. Acoustic a…….

The accordion's evolution balances traditional craftsmanship with modern technology. Acoustic accordions use air pressure and reeds for rich, organic tones, while digital models offer diverse sounds through synthesis and DSP. Both types cater to various musical genres and preferences, making accordions accessible to beginners and appealing to advanced players seeking innovation or classic styles.
“Unleash your inner musician with an exploration of the acoustic vs. digital accordion world! This comprehensive guide delves into the heart of these versatile instruments, dissecting their unique mechanics and sounds. From the intricate dance of traditional acoustic mechanisms to the revolutionary digital technology, we navigate the sonic landscape each offers. Discover how portability, accessibility, and creative possibilities shape preferences, as we unravel the distinct charm and applications of accordions in modern music.”
- The Mechanics of Accordions: Traditional vs. Modern
- – Explanation of how acoustic accordions work
- – Description of digital accordion technology
- Sound and Texture: Acoustic vs. Digital Resonance
The Mechanics of Accordions: Traditional vs. Modern

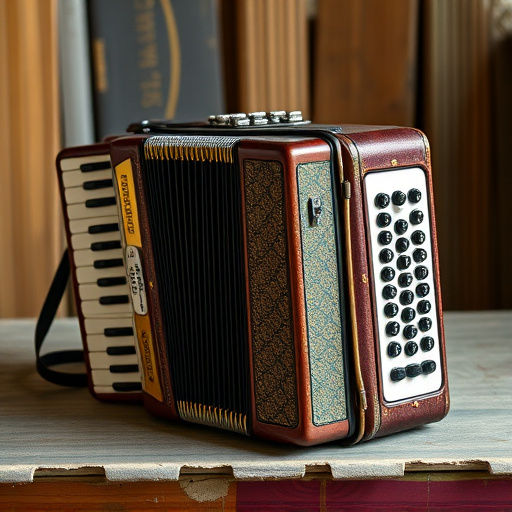
The mechanics of accordions have evolved significantly over time, reflecting a balance between traditional craftsmanship and modern technology. Accordions traditionally feature bellows controlled by buttons or keys, allowing players to generate sound by compressing and expanding air. This manual process requires skill and dexterity, producing a rich, acoustic tone that resonates through the instrument’s body, often made of wood.
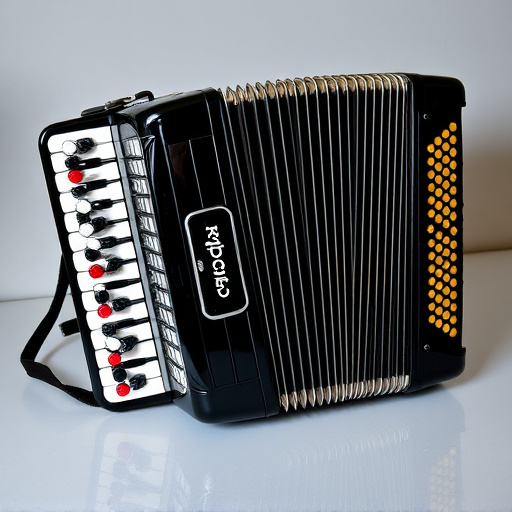
In contrast, digital accordions offer a modern twist with electronic components integrated into their design. These instruments use sensors and synthesizers to convert physical inputs, like button presses and bellows movements, into digital signals that are then processed to produce sound. Digital accordions provide a wide range of sounds and effects, from traditional acoustic tones to synthetic alternatives, accessible through user-friendly interfaces. This evolution has democratized accordion playing, making it more accessible to beginners while preserving the unique characteristics of the instrument for advanced players who appreciate both accordions‘ classical and innovative capabilities.
– Explanation of how acoustic accordions work

Acoustic accordions produce sound through a complex mechanism involving air pressure and reeds. When a musician plays an acoustic accordion, they control the flow of air into the instrument using bellows, which compresses or expands air within its internal chambers. This manipulation activates metal or bamboo reeds, causing them to vibrate at specific frequencies and generate distinct notes. The sound is then amplified through the accordion’s body, producing rich, organic tones that are characteristic of acoustic instruments.
Unlike their digital counterparts, acoustic accordions offer a genuine, unprocessed auditory experience. Each note is crafted by the physical interaction between the musician’s touch and the instrument’s intricate design, resulting in a nuanced and expressive sound. This traditional approach allows for a wide range of musical styles, from folk to classical, where the raw, resonating tones of acoustic accordions can truly shine.
– Description of digital accordion technology

Digital accordion technology represents a modern evolution in the world of musical instruments, offering musicians an innovative and versatile alternative to traditional acoustic accordions. This cutting-edge approach utilizes digital audio processing and synthesis to replicate the sound and playability of an accordion while providing a range of new features and capabilities.
At its core, a digital accordion is an electronic instrument that generates accordion sounds through digital signal processing (DSP) and sample-based technology. Unlike acoustic accordions, which produce sound through the vibration of reeds, digital models use a synthesizer to create realistic accordion tones, allowing for a vast array of sounds and styles to be accessed with just a few buttons or knobs. This technology enables musicians to explore different tunes, instruments, and even experimental sounds, all while maintaining the distinct character and feel of playing an accordion.
Sound and Texture: Acoustic vs. Digital Resonance

When it comes to sound and texture, acoustic accordions offer a rich, full-bodied experience with their natural resonance. Each note vibrates through the instrument’s physical components—reeds, bellows, and strings—creating a complex interplay of tones that can fill a room with warmth and depth. This acoustic quality is often described as having a “soul” due to the organic nature of its sound projection.
In contrast, digital accordions replicate these sounds electronically, aiming to capture the nuances of their acoustic counterparts. While they can mimic many of the natural resonances, digital accordions lack the physical vibrations and ambient interactions that contribute to the unique character of an acoustic instrument. However, digital technology allows for a wide range of sounds and effects, providing musicians with versatility in their performances.